Health information privacy is not only required by the law, but is increasingly important to maintaining patient trust and comfort. Amidst the efforts to secure files with firewalls and doors with badge access, however, one area sinks to the bottom of the list: The waiting room. Healthcare professionals and patients discuss protected health information (PHI), not to mention contact and billing information, well within earshot of other patrons. And while most individuals in the waiting room are too preoccupied to act on this information, it remains a potential breach in the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requirements.
Sound masking is quickly becoming the solution of choice for healthcare facilities attempting to meet federal regulations. The technology renders conversations from across the room unintelligible, suggesting to our brains that we don’t need to listen in. Let’s explore how sound masking can benefit waiting rooms in your facility.
1. HIPAA violations are serious
Congress created HIPAA to protect personal health information in the age of electronic records. Since its inception over two decades ago, the act has received several provisions to further protect the patient while maintaining efficiency and effectiveness. HIPAA audits have also become more stringent. To date, the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) has found 73 cases with HIPAA violations, resulting in penalties totaling over $111 million for the violators. As Reza Chapman from Ernst & Young notes, “It is not a matter of if a hospital will be selected but when,” so it’s best to maintain HIPAA-compliant at all times.
2. Your current methods are ineffective
HIPAA regulations include oral communication of PHI and require that healthcare organizations take “reasonable safeguards” to protect this information. There are four methods of noise control called out by these regulations:
“… reduce noise at the source by selecting quiet equipment and enforcing appropriate office etiquette; absorb noise using absorptive ceiling tiles, wall materials, and flooring, and by limiting the number of reflective surfaces used in the space; block noise using an appropriate layout and partition height…; and cover noise using a sound-masking system.”
Many facilities rely on the physical measures, selecting quiet equipment and noise-absorbing building materials, or the social measures, enforcing appropriate etiquette for the space. But while wall tiles and temporary walls are technically compliant, they aren’t a complete solution. How many times have you been at a clinic and still heard every word that someone has uttered at the counter next to you, or even down the hall? These measures are installed with the best of intentions, but hardly enforce speech privacy.
Other clinics choose to use waiting room music, fountains, or daytime television in an attempt to drown out private conversations. Unfortunately, these sounds only work to compete with conversations, not mask them, requiring individuals to speak louder to be understood over the ambient sound.
3. Your patients demand privacy—from you or your competition
Stating that privacy is important to patients is an understatement. 81 percent of adults report being very or somewhat sensitive about the state of their health and the medications they take, according to the Pew Research Center. Health information is one of the most sensitive sectors of data, joined by social security numbers and phone conversations. Considering these statistics, it’s not a leap to think that a feeling of privacy (or lack thereof) in your waiting room could make the difference between keeping or losing a patient.
81 percent of adults report being sensitive about the state of their health and the medications they take.
This trend is only confirmed by the recent flux of telemedicine, the traditional healthcare industry’s newest competitor. From the comfort and privacy of the home, patients can detail their medical conditions or even video chat with a physician. No need to spend time in the waiting room—or risk someone hearing about the reason for their visit. One of the emerging telemedicine companies, Ro, created apps to help individuals receive treatment for some of most difficult-to-discuss health conditions: Roman targets men experiencing hair loss and erectile dysfunction, while Rory helps women with menopause symptoms.
Although a heightened feeling of privacy can’t remove the stigma from certain medical issues, it can certainly contribute to patient comfort and candor when discussing these topics with healthcare professionals.
Improve patient experience with HIPAA-grade sound masking—get a quote today!
4. Noise management aids patient health
Patients often spend the same amount of time waiting for care as receiving care. Two independent surveys from the Medical Group Management Association and the University of Cambridge found that time in the waiting room and time in the exam room were, on average, the same: 20 minutes. Half of a patient’s experience at your facility is influenced by their time in the waiting room. And no, this isn’t just a question of finding better daytime television.
The negative impact of high noise levels on health is well-documented. In waiting rooms and treatment rooms, the sound of footfall, equipment alarms, and other patients is never-ending. As a result, patients experience elevated blood pressure, decreased rate of wound healing, and a higher incidence of re-hospitalization.
In converse, a patient’s positive experience starts when they walk in the door. The waiting room is an opportunity for hospitals to make a good impression, create a feeling of comfort and privacy, and receive calm patients in the exam rooms.
Half of a patient’s experience at your facility is influenced by their time in the waiting room.
The Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) is a publicly-reported survey of patients’ perspectives in healthcare, created to incentivize hospitals to improve quality of care. While HIPAA regulations are objective and federally mandated, HCAHPS is subjective and based on patient experience. Sound masking can help healthcare facilities increase their HCAHPS score by creating a more comfortable environment, resulting in greater patient satisfaction and health. A better score can also help healthcare facilities retain patients, receive new patients, and receive public investment.
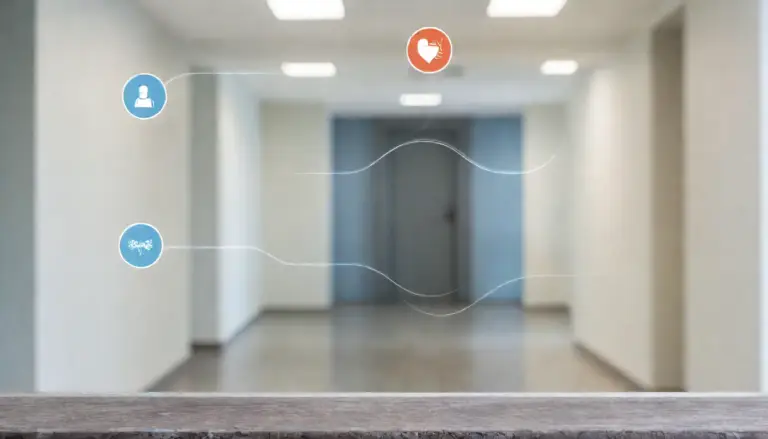
Examine the graphic below. Without sound masking, the entire waiting room can hear John’s reason for visiting the clinic. The sound waves travel easily throughout the space. With sound masking, the sound waves are garbled. Just as you have to strain your eyes to read the text, so would you need to strain your ears to make out the conversation at hand.
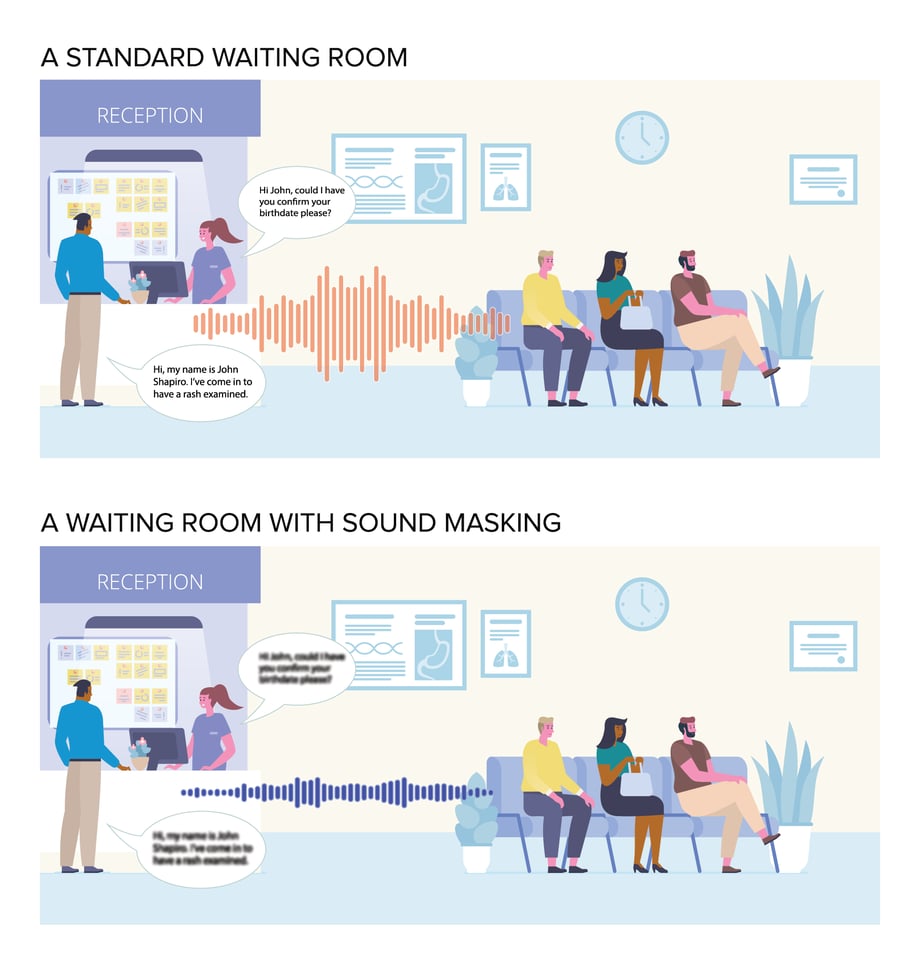
5. Sound masking is effective and easy to install
Sound masking is easy to install in new or existing structures without a large-scale renovation, a significant benefit compared to other acoustic privacy methods. Installation is only as invasive as getting your walls painted, and once installed, sound masking speakers will last for years to come without the need for upkeep.
In deploying frequencies similar to those of a human voice, sound masking makes human speech difficult to understand for other individuals in the room. When individuals notice that they aren’t listening in to other peoples’ conversation, they realize that they, too, have an added layer of privacy. Sound masking also reduces overall noise disruption, leading to a more peaceful environment.
Maintaining health information privacy in the waiting room may make the difference between keeping and losing a patient, or passing or failing a HIPAA audit. While it’s important to assess and address all aspects of the HIPAA audit, with sound masking, you won’t have to worry about your facility’s oral communication privacy or patient experience compliance.
Contact us today to speak with one of our acoustic experts about custom sound masking solutions for your facility. You can discuss your floor plan, describe your unique requirements, and even receive a free quote.









